Partnership for Building Resilience against Public Health Emergencies through Advanced Research and Education (PREPARE)
Initiative to strengthen international networks to tackle infectious diseases
Partnership for Building Resilience against Public Health Emergencies through Advanced Research and Education (PREPARE)
Initiative to strengthen international networks to tackle infectious diseases

Challenges
Millions of people die every year from infectious diseases. The Ebola outbreak in West Africa and the COVID-19 pandemic are recent examples of infectious diseases that have caused enormous socio-economic damage and threaten human safety. Infectious disease control requires a global network among researchers, policy makers and organizations such as governments and laboratories. For several decades, the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) has cooperated with core laboratories in Africa and Asia, which have become important institutions for infectious disease control in their respective countries. JICA’s Partnership for Building Resilience against Public Health Emergencies through Advanced Research and Education (PREPARE) aims to strengthen the network for tackling infectious diseases with these collaborative partners and international organizations.
Towards a Solution
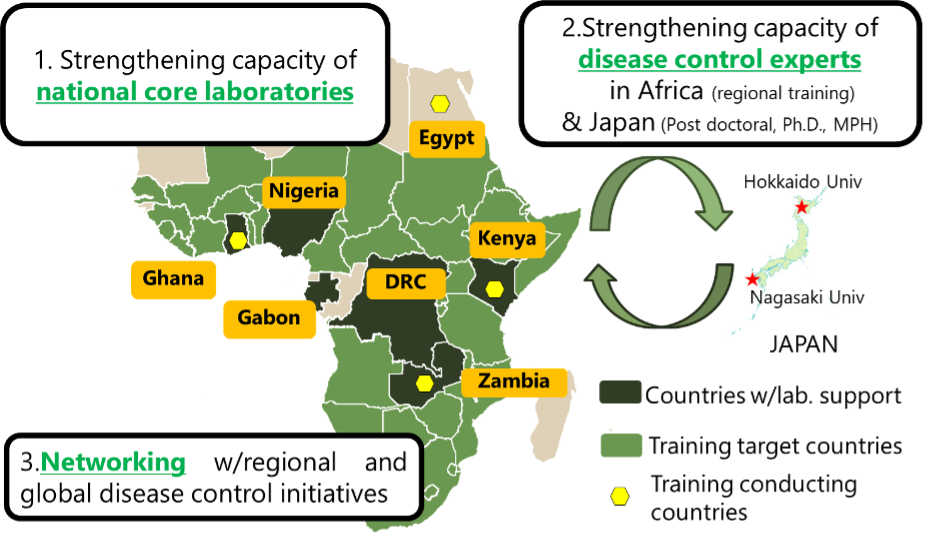
In order to effectively respond to national, regional and global health emergencies, it is essential to build testing capacity and a disease surveillance system. To achieve this and further contribute to the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) on Good health and well-being (SDG 3) and the Istanbul Programme of Action (IPoA) priority area 5 (Human and social development), JICA has been implementing the “Partnership for Building Resilience against Public Health Emergencies through Advanced Research and Education (PREPARE)” project together with local laboratories and academic institutions in developing countries, including least developed countries (LDCs). This project entails the following three components:
- Strengthening the capacity of core national laboratories
Preparedness for health emergencies, such as outbreaks of infectious diseases, is an important element in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC). For many years, JICA has cooperated with several core laboratories, especially in Africa and Asia (e.g., the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, Zambia, the Philippines, and Viet Nam), to develop facilities to address infectious diseases through grant aid and technical cooperation. As a result, human resource capacity and laboratories’ operational capacity have been strengthened and expanded.
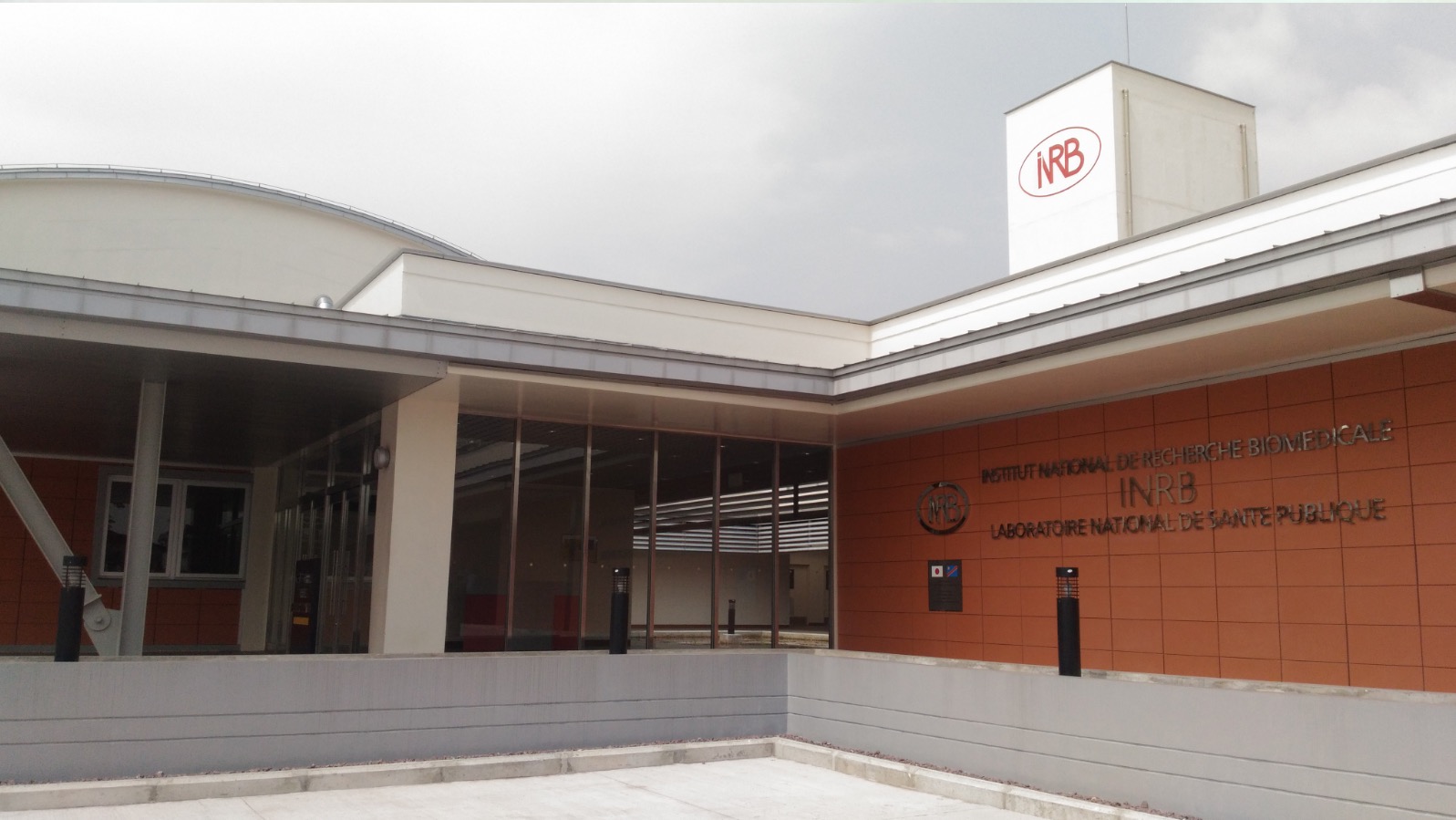
One outstanding example is the Institut National de la Recherche Biomédicale (INRB) in DRC. JICA provided grants to construct testing, research and training facilities including level three biosafety laboratories, in addition to necessary equipment. This has enabled INRB, the only existing national institution in the DRC for fighting infectious diseases, to upgrade its technical platform, shorten diagnosis times and improve its preparedness for epidemics. JICA and INRB also have implemented technical cooperation projects to strengthen the epidemiological surveillance system to promote infectious disease control in DRC.
- Strengthening the capacity of disease control experts
To enhance specialized human resource development, JICA launched a long-term training programme in Japan in 2017, in which participants aimed to acquire a doctorate or master's degree, or conduct research as a post-doctoral researcher in the field of infectious disease control in Japanese universities. Approximately eight participants per year from developing countries, including LDCs such as DRC, Zambia, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, and Viet Nam, join the programme provided by Nagasaki University and Hokkaido University.
Moreover, to widely strengthen surveillance systems in Africa, regional training programmes are offered at four institutions in Africa, namely the Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research (NMIMR) in Ghana, Suez Canal University in Egypt, Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI) and Zambia National Public Health Institute (ZNPHI), to train laboratory technicians and government officials from a wide range of countries in Africa which include LDCs. In January and February 2021, during the COVID-19 pandemic, JICA assisted the NMIMR of Ghana to host third-country online training for nine countries in West Africa, which include LDCs, on countermeasures against infectious diseases, including COVID-19, with the participation of 15 experts as trainees. Through triangular cooperation, JICA and partner organizations with a long-term collaboration history were able to scale up the development impacts accumulated in Ghana, Egypt, Kenya and Zambia to almost all of sub-Saharan countries.
- Networking with regional and global disease control initiatives
Strengthening regional and global partnerships with international organizations is also an important element in enhancing preparedness for health emergencies. JICA is seeking more collaboration with organizations such as WHO, Africa CDC and OIE (the World Organization for Animal Health) because they have specific roles and expertise in norm setting, global/regional strategy formulation and action implementation. JICA is strengthening ties with these organizations to share common objectives towards achieving UHC and building more resilient health systems to respond to health emergencies.
The initiative has strengthened developing countries’ (including LDCs’) surveillance systems, human resources and networks. With better preparedness, countries have been able to respond quickly to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Contact Information
Countries involved
Supported by
Implementing Entities
Project Status
Project Period
URL of the practice
Primary SDG
Secondary SDGs
Similar Solutions
| NAME OF SOLUTION | Countries | SDG | Project Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
A Billion Brains: Smarter Children, Healthier Economies High Level Meeting on South-South Cooperation for Child Rights |
Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Japan, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | 17 - Partnerships for the Goals | Completed | View Details |
Accelerating the Implementation of African Union Treaties in São Tomé and Príncipe South-South learning from the Beninese judicial system’s experience in the application of human rights treaties to its national law |
Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Japan, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | 05 - Gender Equality | Completed | View Details |
Accelerator Labs Network Following collective intelligence methods to address emerging sustainability challenges and the growing demand for local solutions |
Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Japan, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | 08 - Decent Work and Economic Growth 13 - Climate Action | Ongoing | View Details |
Accessibility of Financial Services and the Private Sector in Africa Maximizing the impact of financial cooperation on economic development and industrialization in Africa |
Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Japan, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | 08 - Decent Work and Economic Growth | Completed | View Details |
Accessible Digital Textbooks Promoting inclusive education through Accessible Digital Textbooks |
Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Japan, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | 10 - Reduced Inequalities | Completed | View Details |